Adventure tourism, as defined by the UNWTO, is a type of travel involving exploration or travel to remote areas, where the traveler should expect the unexpected. It typically includes activities with a perceived (and possibly actual) risk, and potentially requires specialized skills and physical exertion.
Adventure tourism has soared in popularity as travelers seek unique and engaging experiences beyond traditional sightseeing. People are drawn to the thrilling aspect of exploring new territories, immersing themselves in diverse cultures, and tackling physical challenges. This form of tourism not only satisfies the craving for adrenaline but also sustains interest in outdoor activities such as trekking, rock climbing, white-water rafting, and scuba diving.
It caters to the desire of tourists to connect with nature, step out of their comfort zones, and discover their limits. Adventure tourism also contributes to the economy of destination areas, often encouraging sustainable practices and conservation efforts. It is a growing niche blending excitement with environmental and cultural respect, appealing to a wide range of globe-trotters.
Adventure Tourism: An Introduction
Imagine standing on the edge of the world, your heartbeat syncing with nature’s vast rhythms. This is the essence of adventure tourism. It mixes thrill with exploration. It invites travelers to step out of comfort zones. People challenge limits and embrace nature’s wild side. Adventure tourism is not just travel. It’s about experiences that inspire and invigorate the spirit.
Meaning According To Unwto
The United Nations World Tourism Organization (UNWTO) describes adventure tourism with precision. They see it as a way to explore while respecting culture and nature. It means getting involved with the environment. It is about daring activities. Tourists gain new insights and experiences. This turns simple holidays into memorable adventures.
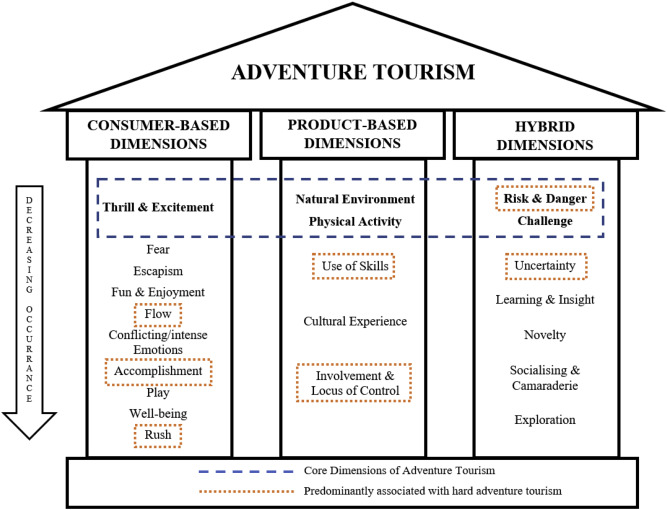
Core Elements Of Adventure Tourism
- Interaction with Nature: Travelers engage deeply with natural surroundings.
- Cultural Exchange: They learn from the locals and their way of life.
- Physical Activity: The journey involves movement, often requiring strength or skill.
These elements define adventure tourism. They ensure it remains a powerful, transformative experience. They make every adventure a story worth telling.

Credit: www.adventurati-outdoor.com
The Evolution Of Adventure Tourism
Adventure tourism inflames the spirit of the curious and the daring. This travel trend blends exploration with exhilaration. It lets tourists plunge into novel experiences with nature and culture as their backdrops. A journey through its evolution reveals a dynamic progression from obscure beginnings to a vast, vibrant industry.
Historical Milestones
Adventure travel has its roots deeply woven into human history. Its timeline stretches from early explorers to modern thrill-seekers. Here’s a glimpse into its pivotal points:
- Age of Discovery: Famous voyages by Columbus and Magellan set the stage. They laid a foundation for adventure tourism.
- Grand Tour: In the 17th and 18th centuries, young European aristocrats traveled for culture and education. This helped shape initial structured travel.
- Mountaineering: By the 19th century, ascents of peaks like Mont Blanc became prestigious adventures.
- Birth of National Parks: The establishment of Yellowstone in 1872 protected nature and welcomed explorers.
- Eco-tourism rise: The late 20th century saw a shift towards environmental conservation and experiential travel.
From Niche To Mainstream
Adventure tourism’s journey from niche interest to mainstream sensation unfolded over decades. A chronological tale of its ascent:
- Specialty Tours: Specialized companies emerged, leading unique expeditions. They catered to those craving a path less traveled.
- Media Influence: TV shows, films, and books about adventures inspired the masses to embark on their own quests.
- Accessibility: Improved travel infrastructure made remote destinations reachable. The world shrank for the intrepid explorer.
- Digital Revolution: Online platforms amplified interest. They helped adventurers research, plan, and connect like never before.
- Burgeoning Market: With growing demand, the industry expanded rapidly. It now features a diverse array of experiences and continues to evolve.
Adventure tourism represents a boon for local economies and a siren call for the bold. Its development into a key sector elevates the traveler’s experience to unprecedented heights.
Categorizing Adventure Travel
Adventure travel invites thrill-seekers and curious explorers to experience the world uniquely. Understanding the categories of adventure tourism helps travelers find their perfect match.
Physical Activity Levels
Adventure trips vary based on physical effort.
- Low impact: Suitable for all ages, includes walking tours and gentle hikes.
- Moderate: Invites more challenge with activities like cycling or kayaking.
- High impact: Targets those in peak fitness, often with extreme sports.
Interaction With Nature
Nature plays a key role in adventure travel.
| Mild Interaction | Immersive Experience |
|---|---|
| Observe wildlife from a distance | Dive into wild landscapes for hands-on exploration |
Cultural Exchange Dimension
Adventure travel also touches the cultural spectrum.
-
Local Learning: Engage with traditional practices and customs.
-
Active Participation: Join community activities, create meaningful interactions.

Credit: www.scribd.com
The Economic Impact Of Adventure Tourism
Adventure tourism is a powerful engine for economic growth worldwide. It goes beyond mere travel. It involves exploring new frontiers, experiences, and cultures. These activities bring vital cash flow and development to host destinations. Let’s explore how adventure tourism significantly benefits local, regional, and national economies.
Boosting Local Economies
Adventure tourism injects money directly into local businesses. These include accommodations, restaurants, and guide services. It also affects small-scale enterprises: local artisans, farmers, and transport providers. The multiplier effect occurs when these businesses flourish. Money circulates numerous times, strengthening the entire economy.
- Rise in tourist spending
- Enhanced infrastructure and facilities
- Renewed interest in local culture and natural resources
Job Creation And Sustainable Practices
As adventure tourism grows, so does the need for skilled workers. New jobs appear across the sector. These range from guides and instructors to conservation and management roles.
Emphasis on sustainability anchors in the heart of adventure tourism. The protection of natural areas ensures long-term viability. It embeds environmental education and sustainable methods into the community. This adoption accelerates green jobs, an up-and-coming segment in job markets.
- Direct employment for locals
- Capacity building and skill development
- Encouragement of conservation efforts
Additionally, many adventure tourism enterprises engage in fair-trade practices. This signals a shift to responsible consumerism. Tourists become part of the solution, not the problem.
Challenges Facing The Adventure Tourism Industry
Adventure tourism thrives on the thrill and excitement of the unknown. Yet, it faces many challenges. These challenges include preserving nature and benefiting local communities.
Environmental Concerns
Adventure tourism often involves travel to untouched natural areas. This can lead to environmental stress. Key concerns include:
- Wildlife disturbances which can change their natural behaviors.
- Trail erosion due to increased foot traffic.
- Pollution, particularly from waste left by tourists.
- Disruption of ecosystems by introducing non-native species.
Operators must minimize their footprint. This ensures sustainable adventure experiences can continue.
Ensuring Local Community Benefits
Adventure tourism can boost local economies. It must be done with care. Fair practices include:
| Benefit | Method |
|---|---|
| Job creation | Hiring local guides and staff |
| Supporting local businesses | Partnering with local suppliers |
| Cultural exchange | Encouraging respectful interactions |
| Economic growth | Ensuring profits benefit the community |
This approach promotes positive impacts for all.
The Future Of Adventure Tourism
Adventure tourism continues to transform as travelers seek unique experiences. This evolution brings changes in technology and global adaption. Thrill-seekers can expect innovative trends to shape their future expeditions. With sustainability and personalization at the forefront, adventure tourism is on the brink of a new era.
Technological Advancements
- Virtual Reality (VR) offers immersive planning tools.
- Drone footage enhances destination previews.
- Wearable tech tracks health metrics during adventures.
Technology elevates the adventure experience before, during, and after trips. VR transforms trip planning into an interactive activity. It allows you to explore destinations from your living room. Drones capture stunning views, enticing more travelers. Wearable gadgets monitor vital signs for safe and informed adventures.
Adapting To Global Changes
- Climate change reshapes natural adventure settings.
- Travelers prioritizes eco-friendly options.
- Local communities become integral to the travel experience.
As the world adapts to climate change, destinations also change. Iconic landscapes may alter, urging us to visit them responsibly. The rise in eco-consciousness leads to a sustainable approach to adventure. Travelers increasingly seek out green options and wish to support local economies. The fusion of travel, ecology, and culture signals a committed step towards responsible tourism.

Credit: www.yodisphere.com
Frequently Asked Questions On Adventure Tourism Definition Unwto
What Is Adventure Tourism?
Adventure tourism involves exploration or travel to remote and exotic locations, offering activities like hiking, rafting, or zip-lining that typically require physical exertion and interaction with nature. It focuses on outdoor thrill and cultural immersion.
What Is The Definition Of Tourism According To Unwto?
The UNWTO defines tourism as the activity of people traveling to and staying in places outside their usual environment for leisure, business, or other purposes for not more than one consecutive year.
What Are The Elements Of Adventure Tourism?
Adventure tourism typically includes elements such as physical activity, cultural exchange, and connection with nature. It often involves exploration or travel to remote areas, challenging experiences, and activities like trekking, climbing, rafting, or wildlife safaris.
What Are The Three Factors Of Adventure Tourism?
Adventure tourism’s three factors are physical activity, cultural exchange, and connection to nature.
Conclusion
Adventure tourism invites thrill-seekers and nature lovers to experience the extraordinary. Defined by the UNWTO, it’s about embracing unique challenges and cultural encounters. As we sign off, remember that responsible adventure tourism enriches lives and conserves our planet. Embrace the call of the wild with respect and anticipation.
Discover, explore, and protect.

Leave A Comment